Describe the Lock and Key Model of Enzyme Action
The lock and key model also called Fishers theory is one of two models which describe the enzyme-substrate interaction. A substrate is bond to.

Effect Temperature On Enzyme Activity Enzymes Activity Biochemistry Enzymes
2 The induced fit model.

. View the full answer. The active site of the enzyme denatures so the substrate can no longer fit it. The key has to match up perfectly to the grooves of the lock or in other words be complementary to them.
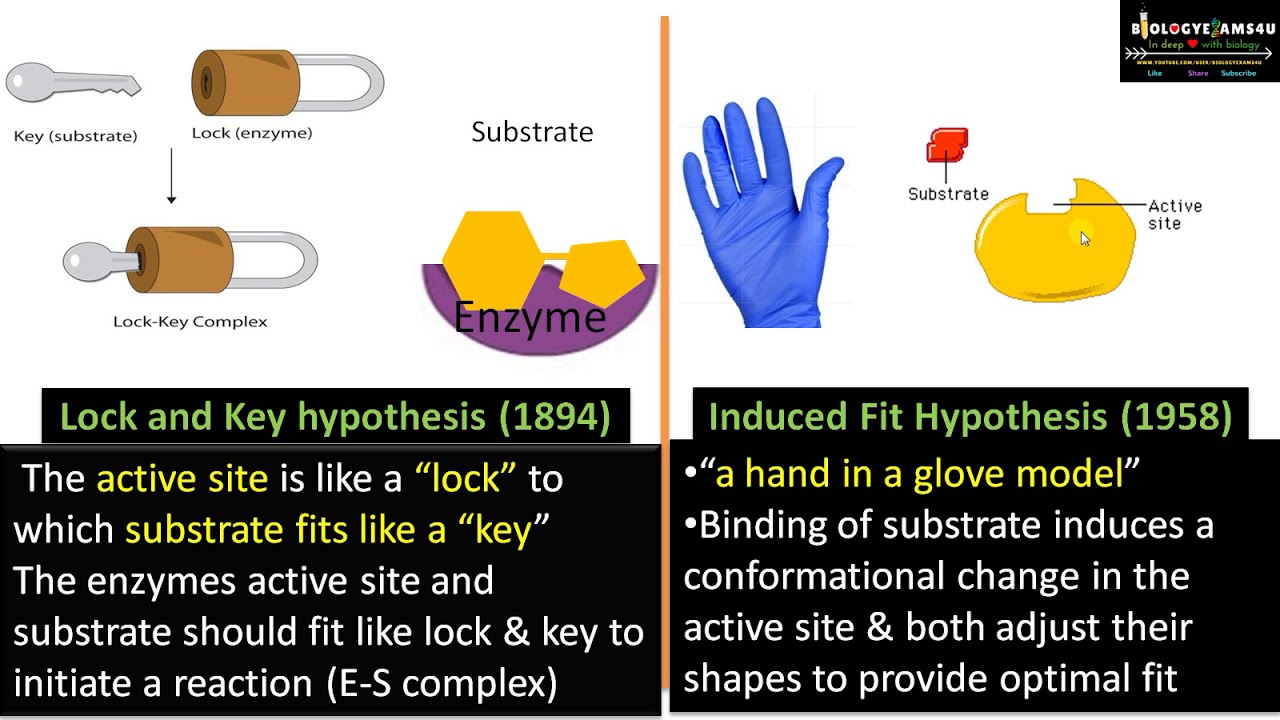
The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the. This model however posed many problems to scientists because such an enzyme-substrate complex would lead to poor catalysis. The lock and key model assumes that the active site of the enzyme and the substrate are equal shaped.
Simply put the lock-and-key model suggests that the shapes of enzymes and reactants fit each other like lock and key. This means they bind easily which helps lower the activation energy. Enzymes are specific for only a certain type of chemical reaction.
This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able. Describe the lock and key model of enzyme action. In fact an early model describing the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex was called the lock-and-key model Figure 1811 The Lock-and-Key Model of Enzyme Action.
It supposes that the substrate fits perfectly into the active site of the enzyme. The lock-and-key model refers to the way in which a substrate binds to an enzymes active site. The specific action of an enzyme with a single substrate can be explained using a Lock and Keyanalogy first postulated in 1894 by Emil Fischer.
The Lock-and-key mechanism was first proposed by Emil Fischer which described as the enzymatic reactions whereby an enzyme with a single substrate binds temporarily to form a substrate complex. The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. It possesses a unique shape that complements that of the substrate.
The lock and key model assumes that the active site of the enzyme and the substrate are equal shaped. What is Lock and Key Model Lock and key model is the second model which describes the enzyme-substrate interaction. Lock and key model Enzymes are.
The shape of the substrate fits the shape of the enzymes active site like a key fits a lock. An enzyme is a protein that functions as a biological catalyst a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction. See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100 3 ratings Question 23 According to the lock and key model enzyme and substrate molecule are complementary in their shape that help them to bind with each other and therefore help in the catalysis by an enzyme.
This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. Figure 1811 The Lock-and-Key Model of Enzyme Action. What does the enzyme action form.
Only the right size and form of the substrate the key. Just as the lock and key model this hypothesis states that the active sites of enzymes act as a lock that has specific molecules such as -COOH and -SH. Fischer has developed a Lock and Key theory to describe the mode of action of the enzyme.
The enzyme is like a lock and substrate is like. It supposes that the substrate fits perfectly into the active site of the enzyme. Therefore it is also called Fishers theory.
This hypothesis explains the specificity of enzymes and also the mode of action of enzymes. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able. According to Fischer enzymes exhibit a high degree of specificity to the substances.
In this analogy the lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate. This model explains enzyme specificity. Lock and Key Model The Lock and Key model is a theory of enzyme action hypothesized by Emil Fischer in 1899.
The active site of an enzyme is a specific region that receives the substrate. In fact an early model describing the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex was called the lock-and-key model A model that portrays an enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to a substrate or substrates that exactly fit the active site. Likewise if the right enzyme fits into the right substrate the drug will form otherwise it wont.
Describe the lock and key model of enzyme action. However Emil Fischer suggested this model in 1894. Fischer has developed a lock and key theory to describe the mode of action of the enzyme.
Just like a lock and key the enzyme as the lock and the substrate as the key is said to fit together. Similar to how a key has to be the correct one for a lock no reaction takes place if an incorrect substrate tries to bind. 1 The lock and key model.
According to the lock and key model the active site of the enzymes serves as the lock while its substrate serves as the key. The enzyme-substrate interaction in the lock-and-key paradigm implies that the enzyme and the substrate have complimentary geometric forms that fit perfectly together. At the moment two models are used to describe enzyme specificity.
Lock and key model of enzyme actionliving in wilmington delaware pros and cons. Explain the lock and key model. Terry cotton fabric characteristics.
April 10 2022. What happens if you heat the enzyme. This model proposes the idea that enzymes are like locks and substrates are the keys to that lock.
The lock and key model assumes that the active site of the enzyme and the substrate are equal shaped. Lock and Key Theory. Only the correctly sized key.
According to this moder both enzyme and substrate possess specific shapes that fit exactly into one another. In this model the enzyme molecule changes shape as the substrate molecules gets close. Most chemical reactions in the body would not be able to take place at all without enzymes.
According to this principle if the right key fits inside the right lock the lock will be opened otherwise it will not. The lock and key model also called Fishers theory is one of two models which describe the enzyme-substrate interaction. In this analogy the lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate.
An enzyme substrate complex. These enzyme molecules can only be opened with the help of specific substrate complexes.

The Structure Of Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough And Smooth Er Diagram Cell Membrane Structure And Function Things Under A Microscope

Miller Levine Chapter 2 Section 4 Video Chapter 2d Part 2 Enzymes Enzymes Reaction Rate Chemical Reactions

5 A Day Revision B4 Enzymes Explain The Lock And Key Model Enzymes Activity Eukaryotic Cell Anaerobic Respiration

What Is A Lysosome Structure Function And Storage Diseases Eukaryotic Cell Organelles Structure And Function

Pin By Michael Davis On Anatomy Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Biochemistry

Mechanism Of Enzyme Action Biochemical Chemical Bond Enzymes

Mitochondria Structure And Function With Diagram Mitochondria Structure And Function Oxidative Phosphorylation

Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Active Site Active Site Biochemistry Teaching Biology

Biology Class 9th Notes Chapter 6 Enzymes Mardan Board 5 Biology Class Active Site Enzymes

Mitochondria And Chloroplasts Worksheet Pdf Download Mitochondria Chemical Energy Worksheets

Lock And Key Model Vs Induced Fit Model Fitness Models Lock And Key Biochemical

Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Choice Questions Biology Notes Lock And Key

Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Enzymes Biology Projects Hypothesis

Enzymes The Induced Fit Model Youtube Enzymes Fitness Models Biochemistry
Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Choice Questions Biology Notes Lock And Key

Lock And Key Model Is Used To Describe The Mechanism Of Enzyme Action This Model Was First Proposed By German Chemist Emil Fisher In 2021 Biology Lesson Video Lessons

Lock And Key Model A Model For Enzyme Action Enzymes Biology Enzymes What Is A Product


Comments
Post a Comment